Sound delay, go away, don’t come back again another day ⛈️
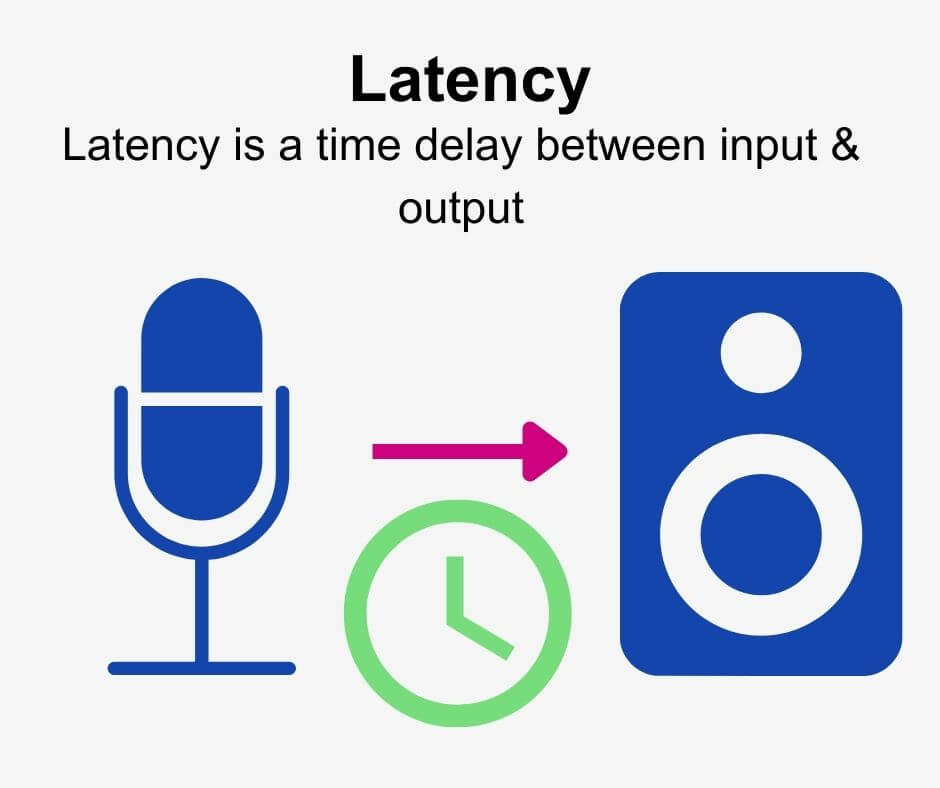
Latency is a time delay (measured in milliseconds) between an input signal entering a recording device, landing on your digital audio workstation timeline, and the output signal leaving speakers or headphones. For further information on audio latency, click here.
There’s many reasons why audio latency can occur, but read on for guidance if you’re having issues. We’ve got a few tricks up our sleeve to help reduce it.
How to troubleshoot audio latency
- Check your computer specifications and make sure your computer can process data fast enough to record audio. To do so, an Intel i5 or equivalent processor and 8GB of RAM are the minimum specifications you should look to meet. However, higher RAM & CPU specifications will further minimize latency.
- Record with a lower sample rate and bit depth. The sample rate is the number of times per second that your computer samples the audio signal. We recommend the following settings for computers with an Intel i5 processor and only 8GB of RAM: Sample rate: 441. kHz, bit depth: 16-bit. A high sample rate and bit depth require more processing from your computer. In other words, you’re asking your computer to take more time to process more data.
- Double-check that your audio interface drivers are up to date.
- Check your cables/speakers. Replace them if you need to! You could also try using a new pair of headphones if you’re experiencing headphone monitoring latency.
How to reduce latency in your DAW
- Reduce the buffer size in your DAW and audio interface settings. A lower buffer size means less latency. But this does mean more processing for your computer which can result in audible glitching for computers with less processing power.
- Buy new cables/speakers if that seems to be the issue. You could also try using a new pair of headphones if you’re experiencing headphone monitoring latency.
- Use ASIO audio drivers. ASIO audio drivers are a type of audio driver that is designed to reduce latency. They are typically available for dedicated audio interfaces.
- Upgrading your CPU and RAM. Though this is usually the least feasible option, utilizing a CPU that’s equivalent to Intel’s i7 and upgrading your RAM to 16GB will go a long way in improving the processing capabilities of your computer.
How to reduce latency in your audio interface
- Use a dedicated audio interface. A dedicated audio interface is a device that connects your computer to your speakers or headphones. It can help to reduce latency by providing its own dedicated processing power for audio.
- Reduce the buffer size in your interface software. But make sure to be careful as too low a buffer size will cause glitches. In contrast, too high will cause audible latency. Therefore you’ll need to experiment with different settings. In general, the more powerful your computer’s CPU and RAM are, the fewer issues you’ll encounter when decreasing the buffer size.
- Utilize zero-latency monitoring if your interface offers it. Audio interfaces that offer zero latency monitoring bypass computer-based latency. As a result, you can directly listen to your input signal through your monitors or headphones before the signal enters the ADC processes.
- Use direct monitoring. By hearing the audio directly from the interface without having to go through your computer can reduce latency greatly.
- Avoid using Bluetooth equipment.
Please note! If you’re still having issues reducing latency, we’d recommend searching online for advice for your specific audio setup.
Check out our blog post for further guidance below!
If you have any further queries, feel free to get in touch with us!
See also:
What’s the difference between analog and digital audio?
What are the audio file requirements?
What is lossless/lossy audio?